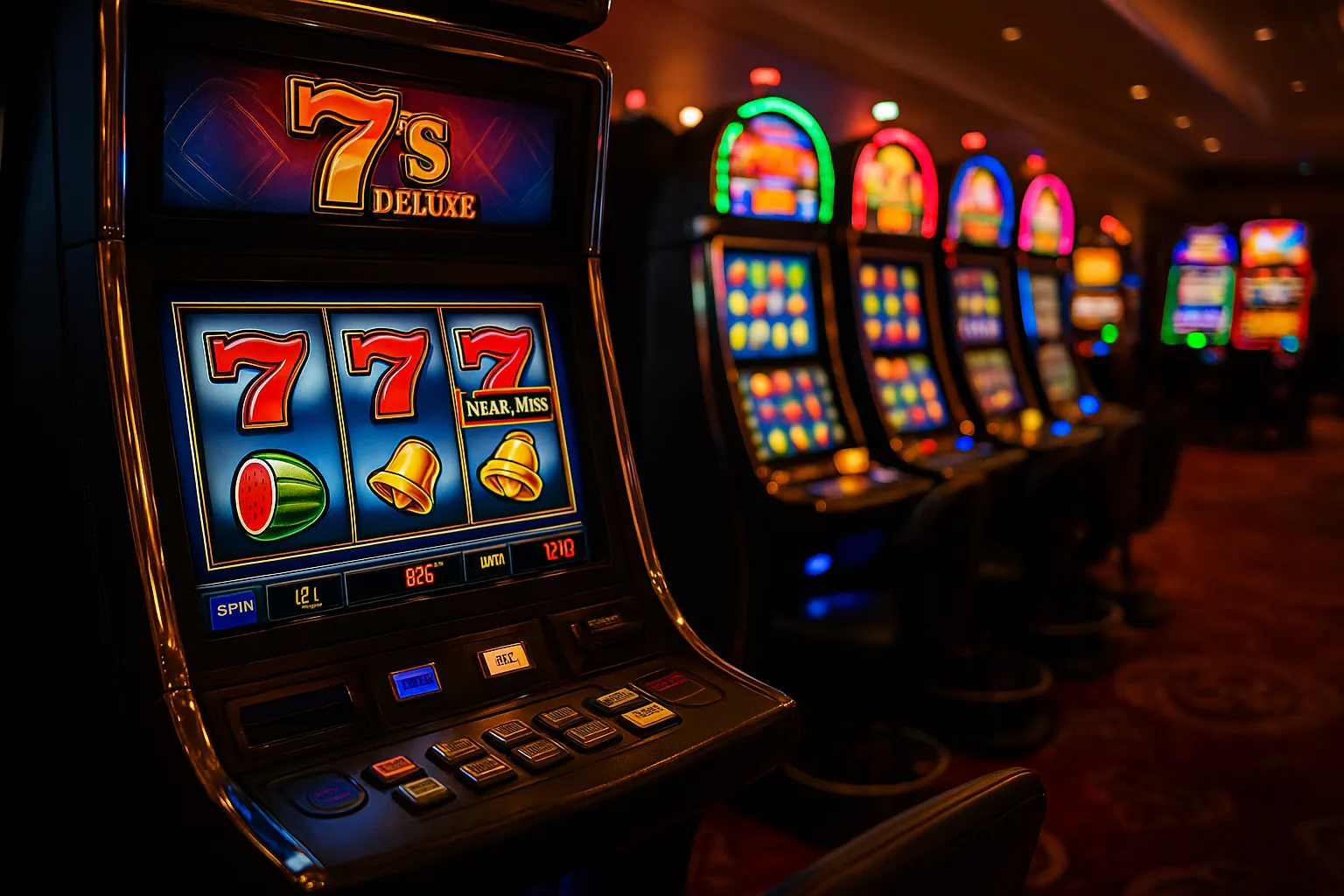
Imagine you’re at a bustling casino, eyes fixed on the spin of the reels. Two matching symbols align perfectly—but the third just misses the payline. That split-second “almost” trigger is called a near-miss, and it’s far from accidental. Game designers and neuroscientists have teamed up to harness this effect, keeping players engaged—and spinning. Let’s dive into the science behind near-miss outcomes in slot machines.
What Is a Near-Miss?
A near-miss occurs when the symbols on the reels stop in a configuration that feels tantalizingly close to a win, but ultimately isn’t. You might see two cherries perfectly aligned, with the third just above or below the payline. While a true win pays out credits, a near-miss delivers nothing—but it tricks the brain into perceiving an almost-win event. Early psychological experiments in the 1950s demonstrated that near-misses in games of chance could increase persistence, even without any financial reward.
The Neuroscience Behind Near-Miss Effects
When a reel stops just inches from a jackpot, your brain lights up as if you’d actually won.
Dopamine Release
Neuroimaging studies show that near-miss outcomes trigger dopamine release in the ventral striatum—the same “reward” circuit activated by real wins. Although there’s no payout, that dopamine surge reinforces the behavior, encouraging you to spin again.
Reward Prediction Error
Our brains constantly predict outcomes. When you expect a loss but almost win, the discrepancy generates a strong neural response. This “prediction error” is interpreted similarly to a real win, driving the desire to continue playing.
In fact, some players seek out non uk casinos because they believe different jurisdictions offer looser regulations on payout rates and near-miss frequencies. While jurisdiction doesn’t change the underlying science, it underscores how near-miss design can be fine-tuned across markets.
How Game Mechanics Create Near-Miss Scenarios
Modern slots rely on Random Number Generators (RNGs) to ensure fairness, yet they can still produce near-misses by design.
Random Number Generators (RNGs)
Every spin generates thousands of random numbers per second. When you hit “spin,” the RNG selects the stopping position for each reel. Developers map symbol probabilities to these outcomes, ensuring that near-miss positions occur more frequently than actual wins—typically at a ratio of 3:1 or higher.
Volatility and Hit Frequency
Slots are configured by volatility (the range between wins) and hit frequency (how often you win). High-volatility games pay large jackpots infrequently, using near-misses to maintain excitement during dry spells. Low-volatility games pay small wins more often, but still leverage near-miss design to keep sessions lively.
Psychological and Behavioral Consequences
Near-misses are more than just design tricks—they affect player psychology in powerful ways.
Illusion of Control
When a reel stops just shy of a jackpot, players often feel they have some control, believing that their timing or “spin skill” matters. This illusion drives repeated play, despite the purely random nature of outcomes.
Persistence and Session Length
Research shows that near-miss events significantly extend playing sessions. A field study found that players exposed to frequent near-misses wagered up to 30 percent more coins per session than those experiencing random losses without near-misses.
Emotional Rollercoaster
Near-misses induce a rush of anticipation followed by frustration. That emotional high-low loop mimics the thrills of a rollercoaster, making slots “hard to put down.”
Responsible Gaming and Mitigation Strategies
While near-misses boost engagement, they can also contribute to problematic gambling behaviors. Industry and regulators have begun exploring ways to mitigate harm.
Transparency in Design
Some jurisdictions require developers to disclose hit frequencies and payout percentages. Transparency helps players make informed decisions and understand that near-misses are coded features, not signs of looming wins.
Session Timers and Reality Checks
Operators can implement session timers that remind players of elapsed time and money spent. Reality check pop-ups help counteract the motivational pull of near-misses by refocusing attention on personal limits.
Self-Exclusion and Betting Limits
Allowing players to set deposit and loss limits in advance empowers them to control spending. Self-exclusion tools can block access for those who feel near-miss effects are driving unhealthy play patterns.
Conclusion
Near-miss outcomes in slot machines are no accident—they’re carefully engineered triggers that tap into our brain’s reward circuits and psychological biases. By understanding the science of dopamine surges, prediction errors, and illusion of control, players can approach slots more mindfully. Meanwhile, responsible-gaming measures and transparent design can ensure that the thrill of the near-miss doesn’t turn into a detrimental gamble.